Starting from v1.1.3, the library is shipped with applications demonstrating how to use the library.
Standalone demo
This is the original command line application, allowing to register two views of the same object or scene. It is available at install_dir/bin/Super4pcs.
To compile, call:
make Super4PCS
See the Usage page for more details.
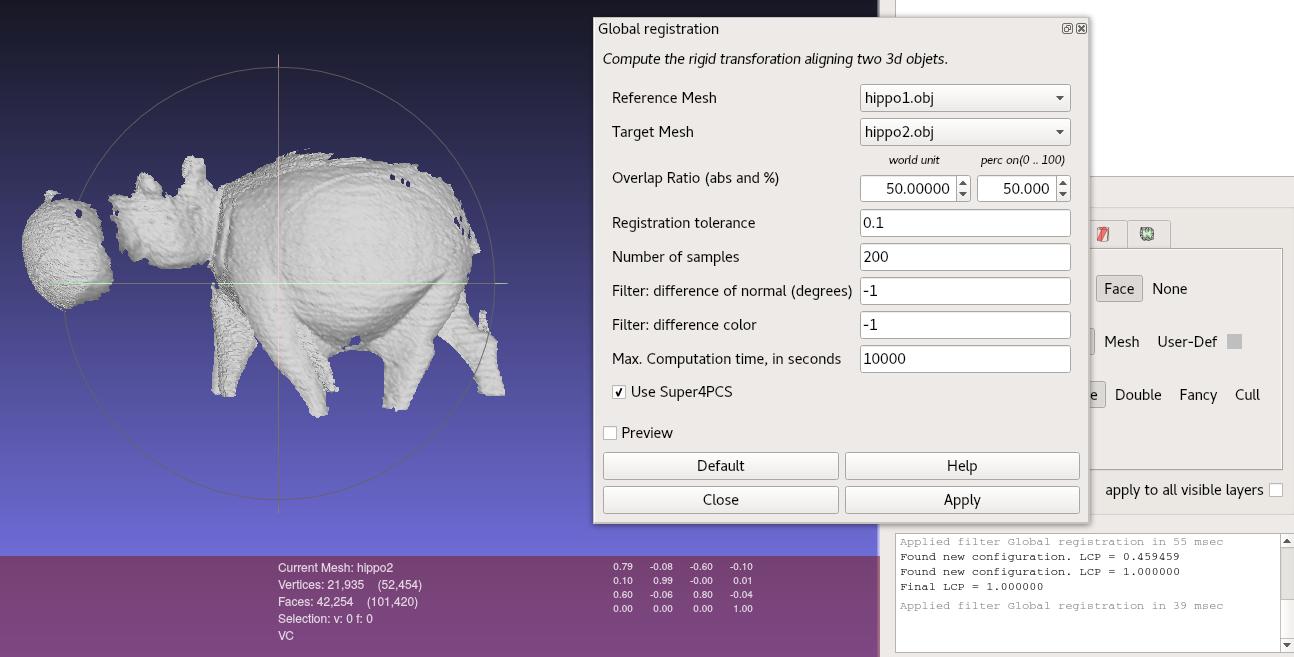
Meshlab Plugin
You need to compile the library from source to use this feature.
A Meshlab plugin can be generated from the library. Since we do not want to carry the full Meshlab repository, we assume that Meshlab source code can be found somewhere close to the Super4PCS sources (check cmake/FindMeshlab.cmake for more details). We thus provide a cmake target Meshlab_install_plugin that will generate a Meshlab plugin source files, and put them in meshlab_dir/src/meshlabplugins/filter_globalregistration:
filter_globalregistration.pro: which properly set the link and include directories to compile the pluginglobalregistration.handglobalregistration.cpp: the plugin source codereadme.md: which gives you the instructions to follow to add the GlobalRegistration plugin to the Meshlab plugin compilation list.
Note that we also copy libraries and include files in the meshlab_dir/src/external folder.
To compile, call
make Meshlab_install_plugin cd meshlab_dir/src # Follow instructions from meshlabplugins/filter_globalregistration/readme.md qmake meshlab_full.pro && make
The plugin can be found in Meshlab in Filter > Point set > Global Registration, or using the filter search engine.
PCLWrapper
Provides a wrapper to use Super4PCS within the Point Cloud Library, and implementing pcl::Registration<PointSource, PointTarget>.
The wrapper source code is available at install_dir/include/pcl/registration. Note that our file structure follows the PCL source code organization.
A command line application demonstrating how to use the wrapper is available here: install_dir/bin/Super4PCS-PCLWrapper. To compile, call:
make Super4PCS-PCLWrapper
The source code of the demo application is quite simple:


 1.8.11
1.8.11